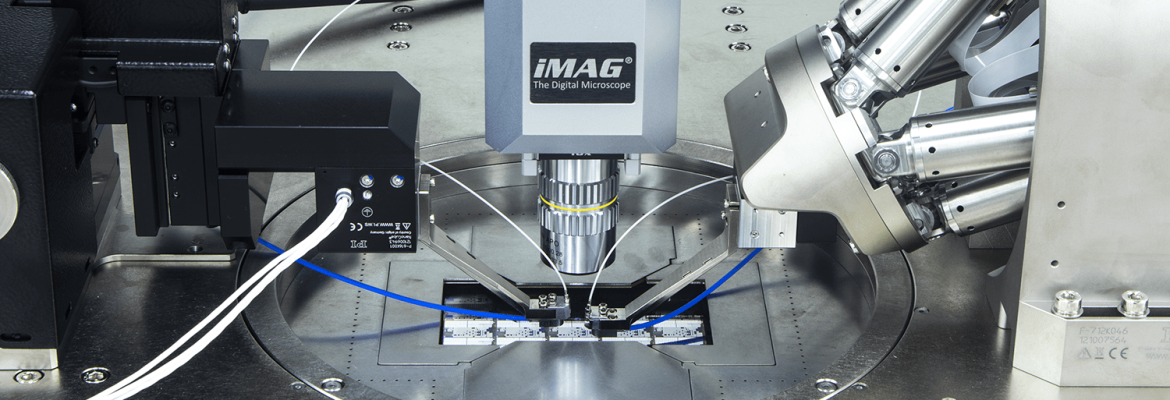
Silicon photonics (SiPH) is a revolutionary technology that enables the integration of photonic devices onto silicon chips.
This technological advancement offers incredible possibilities for optical communications, sensors, and many other applications.
In this article, we will explore the context of silicon photonics applications, the associated challenges, and how MPI products address these challenges with effective and innovative solutions.
Context of Silicon Photonics Applications
Silicon photonics is used to integrate photonic devices directly onto silicon chips, enabling fast and efficient optical communication. This technology is particularly important for data centers, telecommunications networks, and advanced sensing systems. Silicon photonic devices offer high bandwidth, low power consumption, and compatibility with existing semiconductor manufacturing processes.
However, silicon photonics presents several challenges, particularly during the design, validation, and testing phases of the developed technologies: integrating optical fibers for wafer-level testing, precisely aligning fibers with devices, ensuring repeatability of the wafer-fiber distance, preventing collisions between fibers and the wafer, and integrating into test setups. These challenges necessitate advanced solutions to guarantee optimal performance and increased reliability.
Applications of Silicon Photonics
Silicon photonics has a wide range of applications. Here are some of the main ones:
- 1. Optical Communications : Silicon photonic devices are used for high-speed optical communications, enabling fast and efficient data transfers in data centers and telecommunications networks.
- 2. Optical Sensors : Silicon photonic sensors are used for detecting various variables, such as temperature, pressure, and gas levels. These sensors offer high accuracy and fast response.
- 3. Advanced Detection Systems : Silicon photonic devices are used in advanced sensing systems, such as environmental monitoring systems and security devices.
Technological Advances
- 1. Optical Integration on Chip : Silicon photonics enables the integration of photonic devices directly onto silicon chips, offering high bandwidth and low power consumption. This technology allows the replacement of electronic signals with light signals, thereby increasing communication speeds and reducing the energy consumption of communication systems.
- 2. Compatibility with Manufacturing Processes : Silicon is already widely used in the microelectronics industry, which facilitates the integration of silicon photonics into existing manufacturing processes. This enables economies of scale and reduces production costs.
- 3. Energy Impact Reduction : Silicon-based photonic circuits enable a reduction in the energy consumption of communication systems, particularly in data centers, which are major consumers of electrical power. This reduction in energy impact is crucial in a context of growing demand for more sustainable and efficient solutions.
Market Needs
- 1. Growing Demand for High-Speed Communications: With the exponential increase in internet traffic and data (linked to the development of AI), it is essential to have technologies capable of meeting this demand. Silicon photonics offers an effective solution for increasing the speed of information propagation and meeting consumer needs.
- 2. Diversified Applications : Silicon photonics has applications in diverse fields, such as optical communications, medical and environmental sensors, advanced sensing systems, and quantum computing. This versatility contributes to its rapid growth.
- 3. Collaboration and Investments : Companies like TSMC and Nvidia are collaborating to advance silicon photonics, demonstrating the growing interest of major market players in this technology. Furthermore, significant investments are being made to develop advanced testing and packaging facilities..
Concrete Examples of Applications
- Datacenters et Réseaux de Télécommunications : Les dispositifs photoniques sur silicium sont utilisés pour les communications optiques à haute vitesse dans les datacenters et les réseaux de télécommunications. Par exemple, les émetteurs-récepteurs optiques 800G-DR4 OSFP224 d’Innolight sont utilisés dans les réseaux Ethernet 800G, les datacenters et les réseaux cloud.
- 2. Medical and Environmental Sensors : Silicon photonic sensors are used for the detection of medical and environmental variables. For example, SiPH sensors can measure small changes in refractive index caused when light passes through a sample.
- 3. LiDAR : Laser-based remote sensing (LiDAR) devices use silicon photonics to send out a light pulse and measure the return time. This technology is used in autonomous vehicles and mapping systems.
- 4. Quantum Computing : Quantum computers use photons to perform calculations. Silicon photonics enables high-speed and high-precision quantum computing.
MPI's innovative solutions for probe testing of silicon photonic chips
MPI’s SiPH solutions are designed to address typical silicon photonics testing challenges, including optical fiber integration for wafer-level testing, fiber alignment with devices, wafer-fiber distance repeatability, fiber-wafer collision prevention, and integration into test executives.
Photonic Alignment System:
MPI offers multi-channel photonic alignment systems with 6 degrees of freedom for ultra-fast scanning routines, direct optical signal detection, position sensors for high accuracy and operational reliability, and automatic coupling optimization.
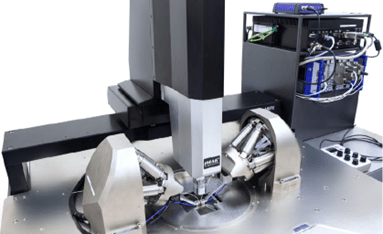
The necessary optical alignment steps, such as the hexapod, are fully integrated into the test station’s control software. They are used just like any other automated positioner, including their additional alignment functions. In addition to being integrated into the multi-touch software, the hardware control panel supports the SiPH positioner type. This makes it easy and highly ergonomic to implement processes for reliable and repeatable optical measurements.
The software for operating automated equipment offers other essential functions for measurements on silicon photonic devices. For example, the user is guided through the entire setup process by a dedicated virtual assistant. And the integrated SmartFence™ function enables safe and convenient manual fiber navigation without the risk of collision.
Manual and Automated Positioning:
MPI offers numerous manual and automatic configuration options to adapt to different test environments and usage constraints. In particular, the manual XYZ translation and 3-axis (UVW) rotation positioning options, combined with an automated nano-positioner system, provide a cost-effective solution perfectly suited to multiple applications, while ensuring high measurement accuracy and repeatability.
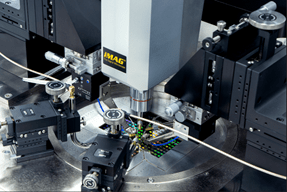
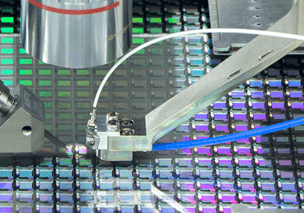
Distance Sensor:
MPI integrates capacitive sensors into the probe arm for precise fiber positioning, with a resolution of 40 nm and a measurement range of 1000 µm. This unique feature enables extremely high accuracy and repeatability of the distance between the optical fiber (or fiber array) and the coupling point, essential for the quality of SiPH measurements.
All MPI SiPH systems include a calibration zone for silicon photonics. Within this zone, the fiber height is calibrated to allow for repeatable fiber placement during chip-by-chip measurement. An optical power sensor measures the fiber output power to accurately determine the optical power delivered to the device under test. MPI offers optical power sensors with a wavelength range of 400 to 1550 nm, a minimum input power of 85 nW, and a maximum input power of 85 mW.
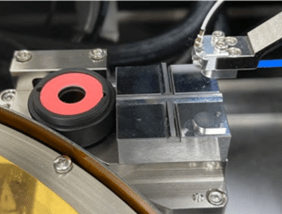
MPI’s solutions overcome the challenges of silicon photonics by offering advanced test systems, precise positioning options, and multiple measurement capabilities. These innovations ensure optimal performance and increased reliability for silicon photonics applications.
Temperature testing of silicon photonic components
Silicon-based photonic components, such as optical transceivers, require rigorous testing to ensure they function correctly at different temperatures.
Needs include:
- Calibration and adjustment to precise temperatures : These tests are performed to calibrate the components at specific temperatures and adjust their performance.
- Final tests at precise temperature : Before being marketed, the components are tested at precise temperatures to guarantee their reliability.
- Industrial tests : These tests are carried out at extreme temperatures, ranging from -40°C to 90°C, to simulate real-world conditions of use.
- Commercial testing : The components are tested at commercial temperatures, generally from 0°C to 70°C, before being put on sale.
Equipment and accessories used
Various equipment and accessories are used to perform these tests:
- Temperature conditioners : Devices such as the MPI TA-5000, TA-3000, and TA-1000 These devices are used to test components at temperatures ranging from -80°C to +225°C. They offer great flexibility and extremely rapid temperature changes, enabling high productivity.
- Compatible accessories : Double-walled glass bell jars, silicone tips, and thermally insulating foams are used to maintain components at specific temperatures during testing.
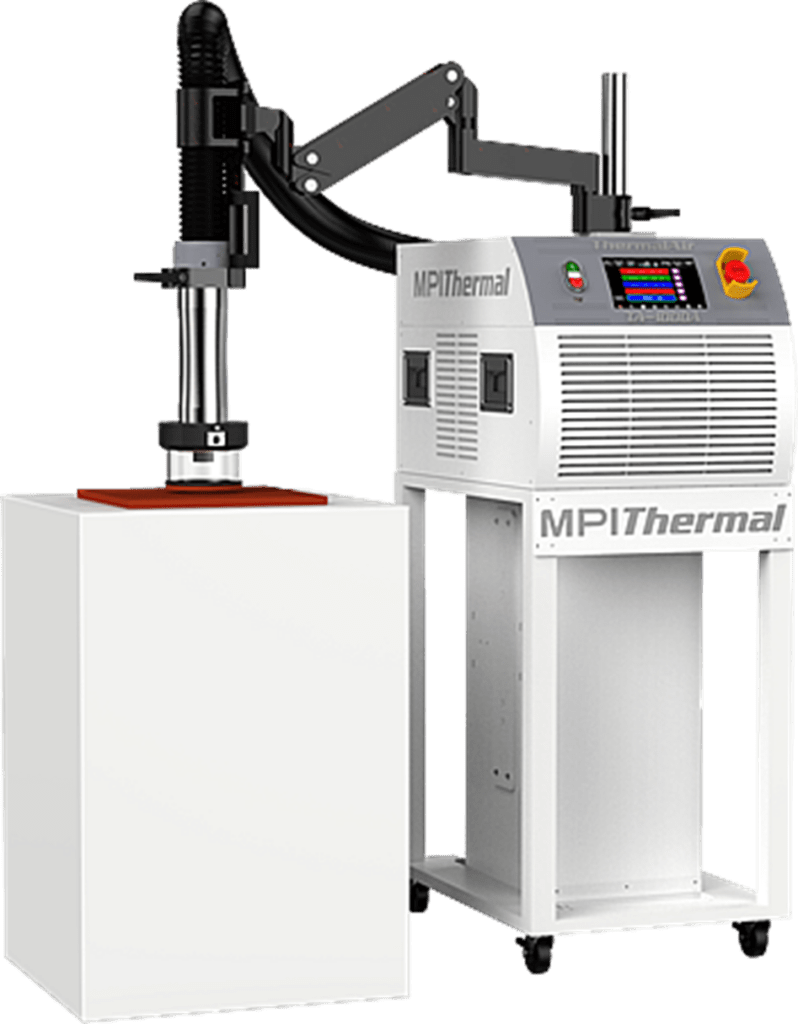
MPI has developed a special range and high-performance integrations, based on their TA-5000, TA-3000, and TA-1000 temperature conditioner series, to enable thermal testing of silicon photonic components in R&D and production. These solutions have been widely deployed in the semiconductor industry due to their user-friendliness, performance, and reliability.
In conclusion, silicon photonics is booming due to its technological advances, its compatibility with existing manufacturing processes, its reduced energy impact, and the growing demand for high-speed communication solutions.
Collaborations and investments in this area also demonstrate the growing interest of major market players in this promising technology. MPI is positioning itself as a key player by offering reliable and efficient solutions tailored to R&D and production applications.